The $324 million bug
In early February, Wormhole, which specializes in cryptocurrencies, was attacked, with hackers attributing $324 million worth of ETH. What could be the reason they were successful? The answer is quite shocking.
Early February, most news sites reported that the cryptocurrency exchange specialist Wormhole Portal had been hacked. The hackers gained 120,000 ETH (Ether), worth $324 million at the time, and a week later, due to the strengthening of ETH against the USD, it is worth approximately $390 million. The question rightly arises: what could have caused such a large-scale theft? The answer is both shocking and thought-provoking at first: a simple if() function, or rather the lack of it in the code.
What is Wormhole and how does it work?
To understand the background of the attack, we need to look a little bit at blockchains and how cryptocurrencies work. Today there are many cryptocurrencies, but not all currency has its own blockchain, several use common blockchains. While the number of cryptocurrencies is around 10,000 at the moment, the number of public blockchains is around 900, the largest of which are Ethereum (ETH), Solana (SOL), Polkadot (DOT), Cardano (ADA). Converting currencies on the same blockchain is a simpler process, but there is also a need to manage the conversion between different blockchains, which is why so-called bridges have been created.
Wormhole Portal is one of the most popular of these bridges, where transactions can be performed between different blockchains, and currencies can be exchanged. During the exchange the bridge binds the amount of cryptocurrency to be transferred into a smart contract on the source blockchain and generates so-called wrapped token on the destination blockchain, as these tokens represent the currencies from other blockchains on the target blockchain, in our case ETH tokens on the Solana chain. The so-called guardians are responsible for the process, who independently validate the steps of the process. The wrapped token will appear on the target blockchain, if at least 2/3 of the guardians have validated the transaction.
The weak point
The hackers used the confirmation messages sent by the guardians to carry out the theft. The hackers figured out that they could generate messages for the Solana blockchain that could bypass signature verification and appeared to be approved previously. Using the code from a previous successful transaction, they generated fake messages to the Solana blockchain, confirming that 120,000 ETH had been committed on the Ethereum chain, so the Solana chain generated 120,000 wrapped ETH tokens for them. What's most shocking about this story is that the whole error was made possible by the lack of a simple 2-line if() function in the code.
Further interesting fact is that an upcoming fix would have indirectly corrected this bug, the latest version of the code with the fix has already been written and released to the public repository on 13 January 2022, to be auditable before the next release. It is possible that the hackers found the bug based on the update and exploited it, but it's also possible that they had knew about this vulnerability earlier and wanted to exploit it quickly before the patch went live.
The missing function in the old and in the new version of code:
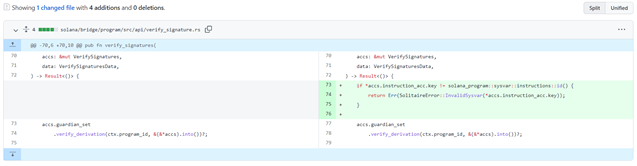
Source: Check instructions sysvar · certusone/wormhole@e8b9181 · GitHub
Afterlife of the attack
The hackers took the 120,000 wrapped ETH tokens, then legally converted most of them back into ETH and disappeared with it. Wormhole has fixed the problem, it continues to operate and has offered the hackers $10 million and full immunity if they return the stolen funds. JumpCrypto, an organisation that supports the advancement and development of crypto, has paid the 120,000 ETH lost, ensuring that there is no deficiency in the system.
This was probably not the last attack on the crypto world. More and more attention is being paid to cryptocurrencies and blockchains, as more and more money is flowing into the segment, making it a market that hackers are increasingly interested in and worth focusing on. According to some sources, in 2021 alone, $2.2 billion have been misappropriated through DeFi (decentralized finance) protocols! So, if you are using or considering implementing a blockchain-based solution, consider the vulnerabilities of blockchain alongside all its benefits.
How can we help you?
We have developed a smart contract audit methodology based on the OWASP standard, which covers the operation of blockchain-based systems from development to operation, using manual controls and various analytical software tools.
Read more about smart contract audit in our previous post: Smart Contract Audit - ABT Treuhand Csoport.
Date: 22. February 2022 | Topic: IT securityIT security
The above summary is provided for information purposes only. We recommend that you consult our experts before making any decision based on this information.
Nexia International is a network combining the expertise and experience of nearly 320 independent tax consulting and audit firms from over 100 countries worldwide and is ranked as the 10th largest such network in the world.

